Regions with the highest number of HIV infected. Official statistics of HIV, AIDS in Russia
This virus is related to those diseases, the news of which for many people is equivalent to the news of a death sentence. Fear of AIDS can be provoked by a real danger, as well as the incurability of the infection, as well as the psychological atmosphere surrounding people with AIDS. For this reason, the consequences of AIDS infection can affect both the physical and mental health of a person. The topic of this article is AIDS, consequences and statistics on the disease in Russia.
AIDS - the consequences of the disease
Physically, infection has a variety of consequences. AIDS, in case of adequate therapy, is treated with advanced antiviral agents, and the patient is able to live for many years with almost no deterioration in living standards. Naturally, with the exception of those consequences of AIDS that are provoked by the therapy itself: the need for regular medication, examinations, etc.
If AIDS therapy is not carried out, or it is insufficient, HIV after years can develop into AIDS, which is much more likely to provoke irreversible changes and cause the death of a sick person.
The psychological blow received by a person in the event of news of an HIV diagnosis, most often, is comparable in depth to a physical illness. Only in recent years, the opinion of society towards AIDS patients has begun to change, they are no longer seen as outsiders and renegades. However, to achieve positive results, work in this direction should be carried out for many years.
AIDS statistics in the world
The virus enters the body through mucous membranes or damaged skin. Therefore, the prevention of the consequences of AIDS implies the creation of a barrier on the viral path in the form of the use of protective equipment, condoms, for example, masks and gloves, the use of only sterile instruments and needles for skin piercing. In the external environment, the virus is unstable, it is negatively affected by high temperature, disinfectants, and even those used in living conditions chlorine-containing preparations.
Excessive use of alcohol and drugs reduces the feeling of control over the safety of injections or sex (the spread of HIV occurs during the use of infected syringes during intravenous drug injections).
Despite the efforts made by the world community to contain the epidemic and take it under control, the spread of HIV infection has gained enormous proportions and is now a real threat to the socio-economic development of most of the world's countries.
Today, according to statistics, more than 40 million people in the world are infected with HIV, of which 15 million people have become infected with AIDS in the past two years alone (which accounted for 37.5% of the total number of people living with HIV) and more than 24 million people died from AIDS.
The danger and scale of the problem of the consequences of AIDS require decision-making at the highest world level. Two specialized Sessions of the UN General Assembly were fully focused on addressing HIV/AIDS issues. We adopted a major political document that defines the main directions of countering the spread of HIV/AIDS not only on a global, but also on a regional scale.
AIDS - statistics in Russia
In Russia, the epidemic situation around the spread of AIDS is not a regional problem. The number of people infected with AIDS in the state exceeds 250,000; they have been registered in almost every subject of Russia. The rate of HIV infection increased by 29.7% from 121 per 100,000 people in 2001 to 15 at the beginning of 2003. The most difficult situation was formed in the metropolitan area, as well as St. Petersburg, Samara, Orenburg, Chelyabinsk regions and the Khanty-Mansiysk Autonomous Okrug.
AIDS, whose prevalence statistics are disappointing, is alarming because intravenous drug users make up approximately 76% of newly registered HIV infected with a certain fact of infection; approximately 70-80% of those infected are young people aged 15-29 years.
Starting from 2001, according to AIDS statistics in Russia, the sexual way of spreading HIV infection has become more active; in 2003, more than 15% of new HIV infections were registered among people who did not use drugs. A significant increase in the sexual route of distribution was noted in the Tver, Kaliningrad, Nizhny Novgorod regions and Krasnodar Territory.
The proportion of women of childbearing (fertile) age has significantly increased in the total composition of HIV-infected people. According to AIDS statistics in Russia, during the entire period of registration of infection (a fifteen-year interval), 6302 children were born from HIV-infected mothers, of which 70% were born in 2003-2003.
14.07.2016 20:33
There are no more risk groups, everyone is infected. And most do not know about it, because we do not accept testing, and condoms are not popular. Meanwhile, the monopolies drive up drug prices. If they do not decrease, and the Russians do not become more careful, by 2020 the number of patients will increase by 250%.
There are already more than a million infected people in our country, and every day there are more and more of them. In some regions, there is not enough money even to provide patients with the minimum necessary therapy. Prices for drugs are rising because 90% of tenders for the purchase are held without competition, and 27 billion rubles of budget money are fraternally divided by several private companies.
A huge paddy wagon with the letters HIV on the license plate is driving through Russia. He stops at the house, the commissars get out of the cabin, break into the apartment and take out another average Russian from there.
- I'm not a drug addict and not a homosexual, I'm not guilty of anything, I have a family, children! he protests.
"It doesn't matter," the commissars say indifferently, and push the new prisoner into the car.
The paddy wagon thundered through the Samara, Irkutsk, Sverdlovsk, Kemerovo regions. There already more than 1.5% of residents are HIV-positive. That is, from each city 10-story building, special vehicles took five residents.
In Leningrad, Ulyanovsk, Tyumen, Chelyabinsk, Orenburg and many other regions -1-1.5% infected among residents. It's hard to find a school there kindergarten that would be bypassed by HIV.
On the map, you can see how the number of infected in relation to the population of regions in Russia has grown.Data for 1994-2014provided by the Federal Scientific and Methodological Center for the Prevention and Control of AIDS (there is no information on Crimea, since then it was not part of Russia).
The share of HIV-infected people in the total number of inhabitants of the region
The epidemic covered Russia unevenly. Half of all those infected live in 20 of the 85 regions.
“In all regions, people live differently. There are more infected people where drugs were supplied in large quantities and where there have long been a large number of infected drug users,” says Vadim Pokrovsky, head of the Federal Scientific and Methodological Center for the Prevention and Control of AIDS.
These are the regions where drug trafficking took place, for example, the Orenburg region. As well as materially prosperous parts of the country where drugs were easier to sell (Irkutsk and Sverdlovsk regions).
Residents are unaware of the threat
HIV has ceased to be a disease of "risk groups" - now it comes to homes ordinary people. Natalia and Ivan— the most common Russian family. The first pregnancy, women's consultation, vitamins, examinations and a mandatory HIV test turned out to be positive for Natalia. Ivan's test also revealed that he had the virus. No drugs, casual relationships, blood transfusions, everything is calm and stable. Where did the virus come from? Ivan divorced his first wife six years ago. Decided to check— She also tested positive for HIV. Before his first marriage, Ivan met a girl - it was she who became the source of the infection. If the analysis had been done seven years ago,three people would have remained healthy.
However, in our country, people do not consider it necessary to be tested. Moreover, they do not think about elementary protection. More than a third of the Russians surveyed by Lifehave never been tested for HIV, which can be done for free at any clinic. about halfdo not use condomswhen having sex.
The survey was conducted jointly with the research company Vengo Consult (2277 people took part).
Spending regions: not enough for one package of medicine
HIV-infected have the right to receive free from the state drugs that suppress the virus. But not everyone gets it. sick or buy expensive drugs themselves, or are not treated at all.And then they die quietly, without protesting on federal highways. Because invirus kills imperceptibly. You don't take medicine and you can feel quite normal. And then you catch the flu - and because of reduced immunity, it turns out to be fatal.
According to Minister of Health Veronika Skvortsova, 37% of those infected are now receiving drugs. In the plans - cover 60% by 2020.
According to Head of the Federal Scientific and Methodological Center for the Prevention and Control of AIDSVadim Pokrovsky, approximately 25% of Russians with HIV receive medication.
IN WHO guidelines state that all infected people should be treated since the discovery of the virus in the blood. But in our country, there are different rules: we begin to treat when the immunity of the infected is already reduced. Immunity can be measured in CD4 cells. In Russia, it is believed: if these cells become less than 350 per 1 cubic mm of blood, then the time has come.An HIV-negative person has 500-1200 of them per 1 cubic mm of blood.
This happens because we simply do not have enough money allocated for treatment, he explained. Vadim Pokrovsky.
According to the press service of the Ministry of Health, this year 23.3 billion rubles have been allocated for the purchase of drugs for HIV-infected people. The money is transferred to the regions, and local authorities purchase drugs through public procurement.
Interestingly, the principle “where more people get sick, there are more drugs” does not work at all. Life analyzed all the tenders for 2014 and calculated how much money each region spends on one infected person.
Amounts allocated by the regions per one HIV-infected person per year
For example, in the Perm region - 23 thousand infected. Drug costs - 14 million rubles(608 rubles per person). In the Vologda Oblast - 2.4 thousand infected, costs - 45 million rubles (19 thousand rubles per person). There are regions where a meager amount is allocated per infected person, including Orenburg (240 rubles per year) and Kaluga (589 rubles per year) regions. This not even enough for a package of ritonavir (one of the most popular drugs, on average costs about 3,000 rubles).
It would seem that good indicators in the Republic of Altai and Stavropol Territory, where one infected person accounts for 30.5 thousand rubles and 43 thousand rubles a year, respectively. But this is still very little.
One year of therapy costs an average of 180 thousand rubles. Four times a year you need to take tests - this is another 40 thousand rubles.
“Money from the federal budget is distributed among the regions in proportion to the number of infected people,” said Vadim Pokrovsky. “And how the regions spend them is another question.”
He also named the factors that can influence the statistics.
“Maybe the region planned to purchase more drugs and more tenders were announced, but no one came to them, because there were unfavorable conditions,” said Vadim Pokrovsky. — If few drugs are purchased, then the price per package increases - this can also affect the total amount. As for the corruption factor, this is not a question for me, but for law enforcement agencies.”
Life sent requests to several regions. The answers came from the Kaluga and Yaroslavl regions. So, the Ministry of Health of the Kaluga region (there is 589 rubles for each sick person per year) reported that drugs are purchased "in accordance with the adjusted budget limits." They assured that residents of the region who have HIV and who need medicines were provided with medicines "on time and in full."
“Treatment coverage was 47% of the number of dispensary HIV-infected patients,” the letter says.
The Department of Health of the Yaroslavl Region (the region spends an average of 2.8 thousand rubles per HIV-positive person per year) responded that the purchases of drugs for those infected “are carried out in a timely manner, uninterrupted provision of patients is organized” and “the full availability of antiretroviral therapy.”
no competition
Medicines could cost less. Just tenders are held without competition in 90% of cases. Life came to this conclusionafter analyzing all 6966 tenders that were held in 2014-2015.The application is usually submitted by only one participant - they conclude a contract with him.
In total, 430 companies supply drugs for HIV-infected people through public procurement. At the same time, 10 leaders take 81% of tenders (27 billion rubles out of 34 billion rubles).
It would seem that they should fight for orders. Because they do not have a division by drugs: they supply similar kits. There is no division by regions either: leaders strive to cover everything at once.
But, for example, the Ministry of Economic Development of Bashkortostan announced a tender for the supply of lopinavir and ritonavir with an initial price of 68.5 million rubles. Only R-Pharm has submitted an application. Of course, he did not offer a lower price. For what? Competitors are still not visible.
The contract agency of the Arkhangelsk region announced a tender for the supply of the same drugs with an initial price of 1.5 million rubles. Only Vitalek applied. He also did not reduce the price - after all, there is no need.
“Participants in a certain market usually have conceptual agreements in which tenders they can participate. This does not mean that participants agree on each tender separately. They can distribute: this group of tenders belongs to me, but this one belongs to you. Although it is possible that someone is negotiating in the corridor for individual tenders. It's a normal process," he says. Pavel Gagarin, Chairman of the Board of Directors of the audit and consulting group Gradient Alpha
“Naturally, they were given a certain matrix, how to play, where to climb, and where not to climb,” he said.
Unraveling the matrix
Firstly, it can be formed by price categories. For example, for lopinavir + ritonavir, R-Pharm usually takes larger orders (average price 10.4 million rubles), while Sanalek, Farmakhan and Vitalek take smaller orders (average price 7 million rubles, 5 million rubles and 3.8 million rubles, respectively.
Secondly, there are brother companies. They have common owners or other signs of affiliation.
Thus, five companies - Sanalek, Vitalek, Unilek and Farmakhan, Plexafarm - are registered at the same address (Moscow, Varshavskoye shosse, 46, A, building 4). Interestingly, the general address is fake. It's just a "rubber" office. According to the Spark database, this address is “indicated as a location during state registration” for 32 legal entities.
The correspondent of Life went to the indicated address and found a small “island” for car lovers: four buildings house auto parts stores, a car wash, and a tire shop. There is also a granite workshop. The old-timers of Avtorrazvilka (this is the name of this complex) claim that there are no offices here and never have been.

“Such a situation, unfortunately, is not uncommon,” says lawyer Yuri Sinelshchikov. - If all violations are revealed, then theoretically it will be possible to qualify the actions of companies as fraud. But only if the damage can be calculated. The damage can be an overpayment of the customer: that is, he bought at the same price, but in fact the price could be lower if another supplier won.
We were not even able to call these companies, although the Spark database lists more than a dozen of their phones. They did not respond to inquiries either.
Another scheme: the co-owner of Vitalek and Farmakhan is Alexei Khavanov, who is also the former co-owner of Sanalek. Unilek and Plexpharm also have a common owner - this is Alexander Maksimov.

It is clear that such brother companies it is easy to agree who takes this or that tender.
Another striking example is the Pharmimex fraternity. There is CJSC Scientific-Production and Commercial Firm Pharmimex. There is a public joint stock company Pharmimex. They have a common owner - Alexander Apazov. Each of the companies has a daughter, for example, Medilon-Pharmimex LLC and Regul-Pharmimex CJSC.
“This industry is ruled by certain officials, companies agree with them on obtaining tenders,” said Pavel Gagarin, chairman of the board of directors of the audit and consulting group Gradient Alpha. - And it will not look very good from the outside if the same company goes to many tenders and wins everywhere. And if companies with different names do it, formally there is nothing to complain about. But it's still a pretty rough game."
Thirdly, there is fake competition in the public procurement market for drugs for HIV-infected people. Here are two "brothers" - Cosmofarm and Medresurs. One of the co-owners of Cosmofarm, Grant Vardanyan, used to have a stake in Jomed. Now Nadezhda Shergalina has a stake in Jomed, and at the same time she is a co-owner of Medresurs.
Kosmofarm and Medresurs often enter the same tenders. And at first glance, the fight seems fair. For example, the State Procurement Committee of the Government of the Khabarovsk Territory published a tender for the supply of efavirenz with an initial price of 1.7 million rubles. Applications were submitted by Kosmofram and Medresurs. Cosmofarm won. And the price of the contract at the same time even decreased - by one percent!
Large figures
Among the market players are people who have good connections. The owner of R-Pharm is 36-year-old Alexei Repik. He is also the president of Delovaya Rossiya, a member of the Public Chamber and a member of the import substitution commission, which Dmitry Medvedev created in 2015. So communication with high-ranking officials is a common thing for him. By the way, he has been working with officials since the age of 16. Then he got a job as an economist in a Moscow hospital and coordinated estimates with the health department. He registered his company R-Pharm when he was 22 years old, that is, 15 years ago.
Pharmstandard is considered the most influential pharmaceutical company in Russia. Chairman of the Board of Directors - Viktor Kharitonin. The 43-year-old businessman is one of the hundred richest people in Russia according to the Forbes Russia magazine rating. The head of the Accounts Chamber, Tatyana Golikova, who was previously the Minister of Health, has been repeatedly accused of lobbying the interests of Pharmstandard. She even got the nickname "Madame Arbidol" (it is produced by "Pharmstandard").
The head of the Pharmimex group is 77-year-old Dmitry Apazov. He is an Honored Health Worker of the Russian Federation. He started working in the system more than 50 years ago. He was the head of the Main Pharmacy Department of the USSR Ministry of Health, and then - CEO association "Soyuzpharmacy" under the Ministry of Health of the USSR. Then Soyuzpharmacia was renamed the state enterprise Pharmimex. In 1995, Pharmimex OJSC was registered.
Will Nacimbio lower prices?
Another major player is about to enter the HIV field. In July 2015, the CEO of the Rostec State Corporation, Sergei Chemezov, sent a letter to President Vladimir Putin with a proposal to make the National Immunobiological Company (Natsimbio), a subsidiary of Rostec, the sole supplier of drugs for HIV-infected, tuberculosis and hepatitis patients in the framework of public procurement.
According to Chemezov, it is necessary to ensure "sovereignty Russian Federation in the field of drug production and import substitution in the domestic drug industry.
A few days later, the president instructed the government to work out the issue. In September 2015, there was another instruction - to return the centralized purchase of drugs for HIV, hepatitis and tuberculosis (previously, the Ministry of Health purchased drugs centrally, and since 2013 the regions began to purchase them).
As Life was told in the press service of the Ministry of Health, the department is already working with Rostec on the topic of HIV. According to the press service, the centralization of public procurement will be "starting from 2017."
According to the press service of Nacimbio, the company plans to reduce the cost of a course of treatment for HIV-infected people by almost half (from the current $1,170 per course to $650). For this, the production of drugs will be organized in Russia. Agreements have been signed with the Indian manufacturer Cipla and the Russian company ChemRar.
Interestingly, when Nacimbio became the sole supplier of anti-tuberculosis drugs for the Federal Penitentiary Service, their prices, on the contrary, increased. So, in May 2016, the Federal Penitentiary Service signed a contract with Nacimbio for the supply of drugs for the treatment of tuberculosis, including ethambutol. The price is 2.8 rubles per 1 gram. In 2013, the Federal Penitentiary Service entered into an agreement for the supply of ethambutol with Medical Leasing Consulting. The price for 1 gram is 2.6, that is, 9% less. But the company itself claims the opposite: before, the Federal Penitentiary Service purchased the drug at a price of 3.4 rubles per gram.
The press service of Nacimbio says that the arrival of the company will radically change the market for drugs for HIV-infected people. Her initiatives “protect the interests of Russian manufacturers” and “in many ways infringe on the interests of domestic distributors who specialize in budget supplies and do not engage in their own production,” they assure.
And now the top 10 are mainly distributors. According to the Spark database, only R-Pharma, Pharmstandard, Pharmimex and Biotechmed have their own production facilities.
Nacimbio's revenue in 2015 amounted to 6.5 billion rubles, net profit - 648 million rubles. The company was established in 2013 - to help in the "development of production in the Russian Federation full cycle medicines." She was given shares in the vaccine manufacturer NPO Microgen, state shares in the pharmaceutical companies Fort and Sintez.
Posters and flyers do not work
“This year, only 400 million rubles have been allocated to inform the population about the threat of HIV,” says Head of the Federal Scientific and Methodological Center for the Prevention and Control of AIDS Vadim Pokrovsky. - This is not enough".
He explained that the money for prevention is distributed by region. As a result, each region receives several million rubles. What are they spending on?
According to the public procurement portal, the authorities of the Belgorod region, for example, ordered "the provision of services to inform the population on the prevention of HIV infection through Internet resources" for 189 thousand rubles. The contractor must place banners "with information about HIV / AIDS on the Internet resources of the Belgorod region." This includes a news site (attendance of at least 100 thousand people per month), social media(on the pages of the local HIV prevention center on the VKontakte and Odnoklassniki networks), an online dating portal.
Also, the performer must create in Odnoklassniki a section called “Psychological Consultation”. There, “users will be able to anonymously ask questions to the psychologist.” And on the VKontakte network, you need to create a heading “From the First Words”, “where HIV-positive people or their relatives can tell their story anonymously.”
“There are no strategic programs to fight AIDS in the regions,” says Vadim Pokrovsky. - As a result, they will print and hang several posters and leaflets - and this is where the prevention ends.
It turns out a vicious circle:
“People don’t even suspect how difficult the situation with HIV infection is in Russia,” notes Vadim Pokrovsky. - Information is the main method of combating the spread of the disease. In addition, it is also cost savings: after all, what less people becomes infected, the less then it will have to be treated.
HIV in the media
In a year and a half (January 2015 to May 2016), the Russian media published 34,627 news reports on HIV.
Key words and phrases: "a antiretroviral therapy and everything connected with it” (3008 news), “l medicine against HIV” (1307 news), “n grip Money"(172 news)," p warnings about the possibility of infection” (108 news), information messages information about what HIV/AIDS is (78 news).
Forewarned is forearmed, but for some reason such weapons don't always work in this war. So far, HIV is winning, and the media are publishing all the new reports from the front: “Since the beginning of the year, 378 people in Udmurtia have become infected with HIV”, “More than 600 Novosibirsk people died of HIV in 2015”.
What to do?
The graph of the growth of HIV incidence in Russia is starting to look more and more like an exponential one. If we do not immediately begin to take measures to reduce the cost of therapy and develop really effective prevention, in addition to printing leaflets and placing banners on websites, the country will “develop a scenario of a generalized HIV / AIDS epidemic, in which by 2020 the number of patients will increase by 250%.”
In the meantime, the process has not begun: look out the window, maybe a paddy wagon with the inscription HIV is already standing at your entrance.
Official statistics of HIV, AIDS in Russia
At the beginning of 2017 The total number of HIV infections among Russian citizens has reached 1,114,815 people(in the world - 36.7 million HIV-infected). Of them died for different reasons 243,863 HIV-infected according to the monitoring form of Rospotrebnadzor "Information on measures to prevent HIV infection, hepatitis B and C, identify and treat HIV patients." In December 2016, 870,952 Russians were living with a diagnosis of HIV infection. As of July 1, 2017 the number of HIV-infected people in Russia amounted to 1 167 581 people, of which 259,156 people died for various reasons ( in the 1st half of 2017 years already dead 14 631 HIV-infected that 13.6% more than for 6 months of 2016.). Population stricken rate RF HIV infection in 2017 was 795,3 infected with HIV per 100 thousand of the population of Russia.
In 2016. It revealed 103 438 new cases of HIV infection among Russian citizens (excluding those identified anonymously and foreign citizens), which is 5.3% more than in 2015 the annual growth averaged 10%. HIV incidence rate in 2016 made up 70.6 per 100 thousand population.
In terms of the rate of growth in the incidence of HIV infection, Russia has taken 3rd place after the Republic of South Africa and Nigeria.
For the 1st half of 2017 in Russia revealed 52 766 HIV-infected citizens of the Russian Federation. HIV incidence rate in 1st half of 2017 made up 35,9 cases of HIV infection per 100,000 population. Most new cases in 2017 were detected in the Kemerovo, Irkutsk, Sverdlovsk, Chelyabinsk, Tomsk, Tyumen regions, as well as in the Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug. Increasing the rate of growth of new cases HIV infections in 2017(but the overall incidence of HIV infection is low) is observed in the Vologda Oblast, Tyva, Mordovia, Karachay-Cherkessia, North Ossetia, Moscow, Vladimir, Tambov, Yaroslavl, Sakhalin and Kirov regions.
Growth in the total (cumulative) number of registered cases of HIV infection among Russian citizens from 1987 to 2016
HIV in regions and cities
In 2016, in terms of incidence in the Russian Federation The following regions and cities were in the lead:
- Kemerovo region (228.8 new cases of HIV infection were registered per 100,000 population — total 6,217 HIV-infected), including in the city Kemerovo 1,876 HIV-infected.
- Irkutsk region (163.6% 000 - 3,951 HIV-infected). In 2017, 1,784 new HIV-infected people were detected in the Irkutsk region over 5 months. In 2016 in the city Irkutsk registered 2 450 new infected with HIV, in 2017 - 1,107. Almost 2% of the population of the Irkutsk region are infected with HIV.
- Samara region (161.5% 000 - 5,189 HIV-infected, including in the city of Samara 1,201 HIV-infected), for 7 months of 2017 - 1,184 people. (59.8% 000).
- Sverdlovsk region (156.9% 000 - 6,790 HIV-infected), including in the city of Yekaterinburg 5,874 HIV-infected (the most HIV-infected city in Russia / Or well reveal? ed./).
- Chelyabinsk region (154,0%000 — 5,394 HIV-infected),
- Tyumen region (150.5% 000 - 2 224 people - 1.1% of the population), for the first half of 2017, 1,019 new cases of HIV infection were detected in the Tyumen region (an increase of 14.4% compared to the same period last year, then 891 HIV-infected people were registered), incl. 3 teenagers. The Tyumen region is one of the regions where HIV infection is recognized as an epidemic.
- Tomsk region (138.0% 000 - 1 489 people.),
- Novosibirsk region (137.1% 000) regions (3 786 people.), incl. in the city Novosibirsk 3 213 HIV-infected.
- Krasnoyarsk Territory (129.5% 000 - 3 716 people.)
- Perm Territory (125.1% 000 - 3 294 people.)
- Altai Territory (114.1% 000 - 2 721 people.)
- Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug (124.7% 000 - 2010 people)
- Orenburg region (117.6% 000 - 2 340 people), in 1 sq. 2017 - 650 people (32.7% 000).
- Omsk region (110.3% 000 - 2 176 people.), for 7 months of 2017, 1184 cases were detected, the incidence rate was 59.8% 000.
- Kurgan region (110.1% 000 - 958 people.)
- Ulyanovsk region (97.2% 000 - 1 218 people.), in 1 sq. 2017 - 325 people (25.9% 000).
- Tver region (74.0% 000 - 973 people.)
- Nizhny Novgorod region (71.1% 000 - 2 309 people.) areas, in 1 sq. 2017 - 613 people (18.9% 000).
- Republic of Crimea (83.0% 000 - 1 943 people),
- Khakassia (82.7% 000 - 445 people),
- Udmurtia (75.1% 000 - 1 139 people.),
- Bashkortostan (68.3% 000 - 2 778 people.), in 1 sq. 2017 - 688 people (16.9% 000).
- Moscow (62.2% 000 - 7 672 people)
Note: %000 is the number of HIV-infected people per 100,000 people.
Leading cities in terms of the number of identified HIV-infected people and the incidence of HIV infection: Yekaterinburg, Irkutsk, Kemerovo, Novosibirsk and Samara.
Subjects of the Russian Federation most affected by HIV infection.
The most significant growth (speed, growth rate of new HIV cases per unit of time) incidence in 2016 was observed in Republic of Crimea, Karachay-Cherkess Republic, Chukotka Autonomous Region, Kamchatka Territory, Belgorod, Yaroslavl, Arkhangelsk Regions, Sevastopol, Chuvash, Kabardino-Balkarian Republics, Stavropol Territory, Astrakhan Region, Nenets Autonomous Region, Samara Region and Jewish Autonomous Region.
Number of newly diagnosed cases of HIV infection among Russian citizens in 1987-2016

afflicted HIV infection of the population of Russia as of December 31, 2016 amounted to 594.3 per 100 thousand people Cases of HIV infection have been registered in all subjects of the Russian Federation. In 2017, the incidence was 795.3 per 100,000 of us.
A high incidence of HIV infection (more than 0.5% of the total population) was registered in the 30 largest and predominantly economically successful regions, where 45.3% of the country's population lived.
Dynamics of prevalence and incidence of HIV infection in the population of the Russian Federation in 1987-2016

To the most affected regions of the Russian Federation relate:
- Sverdlovsk Region (1,647.9%,000 people living with HIV were registered per 100,000 population - 71,354 people. In 2017, there were already about 86,000 people infected with HIV), including in Yekaterinburg more than 27,131 HIV-infected people have been registered, i.e. every 50th city dweller is infected with HIV It's a real epidemic. Serov (1454.2% 000 - 1556 people). Infected with HIV - 1.5 percent of the population of the city of Serov.
- Irkutsk region (1636.0% 000 - 39473 people). Total identified HIV-infected at the beginning 2017- 49,494 people, at the beginning of June (almost six months) 2017 51,278 people were registered with a diagnosis of HIV infection. IN the city of Irkutsk more than 31,818 people have been identified for all the time.
- Kemerovo region (1582.5% 000 - 43000 people), including in the city of Kemerovo more than 10,125 patients with HIV infection have been registered.
- Samara region (1476.9% 000 - 47350 people),
- Orenburg region (1217.0% 000 - 24276 people) regions,
- Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug (1201.7% 000 - 19550 people),
- Leningrad region (1147.3% 000 - 20410 people),
- Tyumen region (1085.4% 000 - 19768 people), as of July 1, 2017 - 20787 people.
- Chelyabinsk region (1079.6% 000 - 37794 people),
- Novosibirsk region (1021.9% 000 - 28227 people) region. As of May 19, 2017 in the city of Novosibirsk more than 34 thousand HIV-infected people have been registered - every 47 resident of Novosibirsk has HIV (!).
- Perm Territory (950.1% 000 - 25030 people),
- G. Saint Petersburg(978.6% 000 - 51140 people),
- Ulyanovsk region (932.5% 000 - 11728 people),
- Republic of Crimea (891.4% 000 - 17,000 people),
- Altai Territory (852.8% 000 - 20268 people),
- Krasnoyarsk Territory (836.4% 000 - 23970 people),
- Kurgan region (744.8% 000 - 6419 people),
- Tver region (737.5% 000 - 9622 people),
- Tomsk region (727.4% 000 - 7832 people),
- Ivanovo region (722.5% 000 - 7440 people),
- Omsk region (644.0% 000 - 12741 people), as of August 1, 2017, 16 099 cases of HIV infection were registered, the incidence rate is 813.7% 000.
- Murmansk region (638.2% 000 - 4864 people),
- Moscow region (629.3% 000 - 46056 people),
- Kaliningrad region (608.4% 000 - 5941 people).
- Moscow (413.0% 000 - 50909 people)
Age structure
Most high level affected HIV infection of the population is observed in the group 30-39 years old, 2,8% Russian men aged 35-39 lived with an established diagnosis of HIV infection. Women become infected with HIV in more than young age, already in the age group of 25-29 years, about 1% were infected with HIV, the proportion of infected women in the age group of 30-34 years is even higher - 1.6%.
Over the past 15 years, the age structure among newly diagnosed patients has changed radically. In 2000, 87% of patients were diagnosed with HIV before the age of 30. Adolescents and young people aged 15-20 years accounted for 24.7% of newly diagnosed HIV infections in 2000, as a result of an annual decrease in 2016, this group was only 1.2%.
Age and sex of HIV-infected people.

HIV infection was predominantly detected in Russians aged 30-40 years (46.9%) and 40-50 years (19.9%), the share of young people aged 20-30 decreased to 23.2%. An increase in the proportion of newly diagnosed cases was also observed in older age groups cases of sexually transmitted HIV infection in old age have become more frequent.
It should be noted that at low testing coverage of adolescents and youth, more than 1100 cases of HIV infection are registered annually among people aged 15-20 years. According to preliminary data the largest number of HIV-infected adolescents (15-17 years old) was registered in 2016 in Kemerovo, Nizhny Novgorod, Irkutsk, Novosibirsk, Chelyabinsk, Sverdlovsk, Orenburg, Samara regions, Altai, Perm, Krasnoyarsk territories and the Republic of Bashkortostan. The main cause of HIV infection among adolescents is unprotected sex with an HIV-infected partner (77% of cases in girls, 61% in boys).
Structure of the dead
In 2016, 30,550 (3.4%) patients with HIV infection died in the Russian Federation (10.8% more than in 2015) according to the Rospotrebnadzor monitoring form “Information on measures to prevent HIV infection, hepatitis B and C, detection and treatment of HIV patients”. The highest annual mortality was registered in the Jewish Autonomous Region, the Republic of Mordovia, the Kemerovo Region, the Republic of Bashkortostan, the Ulyanovsk Region, the Republic of Adygea, the Tambov Region, the Chukotka Autonomous District, Chuvash Republic, Samara Region, Primorsky Territory, Tula Region, Krasnodar, Perm Territories, Kurgan Region.
Treatment coverage
At the dispensary in specialized medical organizations in 2016 there were 675,403 patients infected with HIV, which amounted to 77.5% of the number of 870,952 Russians living with a diagnosis of HIV infection in December 2016, according to the monitoring form of Rospotrebnadzor.
In 2016, 285,920 patients received antiretroviral therapy in Russia, including patients who were in places of deprivation of liberty. In the 1st half of 2017 received antiretroviral therapy 298 888 patients, about 100,000 new patients were added for therapy in 2017 (drugs for all most likely will not be enough, because the purchase was according to the figures of 2016). Treatment coverage in 2016 in the Russian Federation was 32.8% of the number of registered persons diagnosed with HIV infection; among those on dispensary observation, 42.3% of patients were covered by antiretroviral therapy. The achieved treatment coverage does not play the role of a preventive measure and does not allow to radically reduce the rate of spread of the disease. The number of patients with active tuberculosis in combination with HIV infection is growing, the largest number of such patients is registered in the regions of the Urals and Siberia.
HIV testing coverage
In 2016 in Russia there were tested for HIV 30 752 828 blood samples from Russian citizens and 2,102,769 blood samples from foreign citizens. The total number of tested serum samples of Russian citizens increased by 8.5% compared to 2015, while among foreign citizens it decreased by 12.9%.
In 2016, the maximum number of positive results in Russians in the immunoblot for the entire history of observation - 125,416 (in 2014 - 121,200 positive results). The number of positive results in the immunoblot includes those identified anonymously, not included in the statistical data, and children with an undifferentiated diagnosis of HIV infection, therefore it differs significantly from the number of newly registered cases of HIV infection.
For the first time, 103,438 patients tested positive for HIV. Representatives of vulnerable groups of the population in 2016 made up an insignificant part of those tested for HIV in Russia - 4.7%, but among these groups 23% of all new cases of HIV infection were detected. When testing even a small number of representatives of these groups, it is possible to identify many patients: in 2016, among the examined drug users, 4.3% of HIV-positive people were detected for the first time, among MSM - 13.2%, among contact persons during epidemiological investigation - 6.4%, prisoners - 2.9%, STI patients - 0.7%.
Transmission path structure
In 2016, the role of sexual transmission of HIV infection has grown significantly. According to preliminary data, among those newly identified in 2016 HIV-positive with established risk factors for infection, 48.8% were infected through drug use with non-sterile instruments, 48.7% - through heterosexual contacts, 1.5% - through homosexual contacts, -0, 45% were children infected from mothers during pregnancy, childbirth and breastfeeding. The number of children infected through breastfeeding is growing: in 2016, 59 such children were registered, in 2015 - 47, 2014 - 41 children. In 2016, 16 cases were registered with suspected infection in medical organizations when using non-sterile medical instruments and 3 cases when blood components were transfused from donors to recipients. Another 4 new cases of HIV infection in children were likely associated with the provision of medical care in the CIS countries.
Distribution of HIV-infected people by means of infection.

conclusions
- In the Russian Federation in 2016, the epidemic situation of HIV infection continued to worsen and the trend continues in 2017, which may even affect the resumption of the global HIV epidemic, which, according to the UN report in July 2016, began to decline.
- The incidence of HIV infection remained high, the total number and number of deaths of HIV-infected people increased, and the emergence of the epidemic from vulnerable groups of the population into the general population intensified.
- With the current rate of HIV infection spreading and the lack of adequate systemic measures to prevent its spread, the forecast for the development of the situation remains unfavorable.
- It is required to intensify organizational and preventive measures to counteract the HIV epidemic in the country.
A real AIDS epidemic has begun in Russia - a critical level of HIV incidence has already been recorded in 10 regions of the country, as officially reported in the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation.
According to the data announced by the Minister of Health Veronika Skvortsova, in 57% of cases, the source of HIV infection is injections of "dirty" syringes, mainly among heroin addicts. At the same time, the most deplorable situation is observed in the regions of Russia located on the routes of major drug trafficking channels.
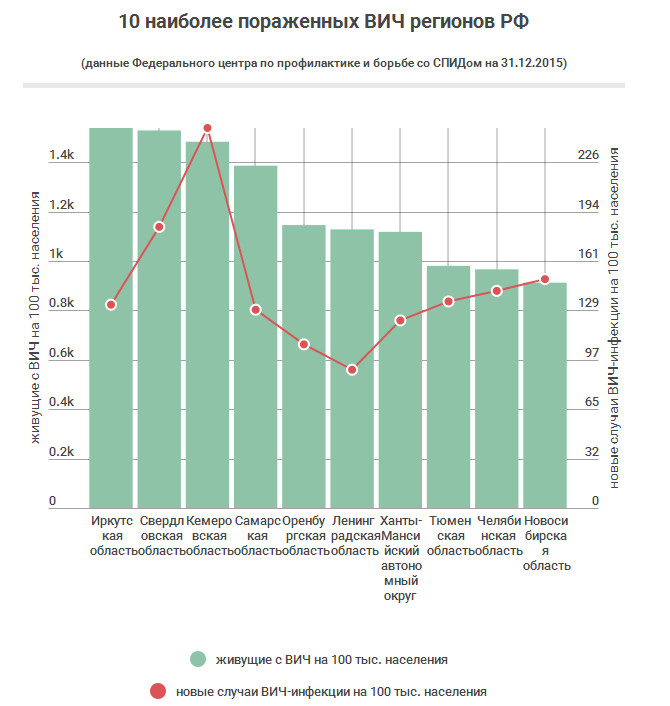
The most critical situation with the incidence of HIV in 2016 is observed in the Irkutsk, Sverdlovsk, Samara and Kemerovo regions, where from 1500 to 1700 people are already infected with HIV for every 100 thousand of the living population.
At the same time, for Last year the rate of new cases of the disease has sharply increased - the record holder here is the Kemerovo region, where 234.5 cases of infection per 100 thousand of the population were recorded per year. According to estimates, if this rate is maintained, the number of infected people in the region will double in just 6 years.
 Statistics on the growth of AIDS incidence in Russia
Statistics on the growth of AIDS incidence in Russia In medium and large cities, the HIV situation is usually worse than in countryside. The authorities of Yekaterinburg, for example, admitted that already one out of every 50 residents of the city is infected. That is, for clarity, we can imagine that in every filled city trolleybus or bus there is at least one person with HIV.
As is known from general statistics, as of January 1, 2016, there were officially 1,006,388 citizens living in Russia who were registered as infected with HIV. At the same time, 212,578 HIV-infected people died in 2015, which is 12.9% more than in 2014 (27,564 people).
In the opinion of Academician Pokrovsky, a well-known Russian expert on AIDS, in fact, at least 1 million more unregistered patients can be safely added to the 1 million officially infected with HIV. At the same time, only 30% of the first million try to be treated at least somehow.
The reason is the banal absence in Russia of clinics with HIV treatment programs, for which funds are simply not allocated. The country's main federal center for AIDS prevention, located in Moscow, is in a state of disrepair. And the government and the Ministry of Health for all the years have not even managed to create a suitable Internet resource with systematized information for the infected, databases of clinics and rehabilitation programs offered to patients.
According to Pokrovsky, only emergency measures with funding of at least 100 billion rubles can save the situation in Russia with the AIDS epidemic. And their effective distribution in three areas - prevention, detection and treatment. However, according to preliminary data for 2017, the Ministry of Health does not provide for such funds in the budget.




