The smallest planet from the sun. The most famous comet. Nearest star cluster
Since ancient times, people have looked at the sky and stars, predictions were made from them, locations were determined, etc. Scientists are working on the study of planets and stars. Which planet is the smallest?
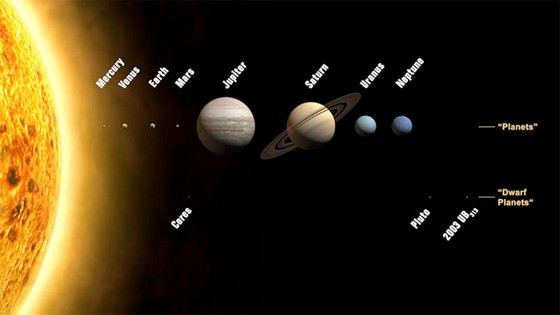
Planets smaller than Earth
You can compare the Earth with other planets in the solar system. Much smaller than our planet is Mercury. It is the first planet from the Sun. It is quite difficult to see, which is due not so much to its miniature size as to its small angular distance to the Sun. Scientists were able to compile its full map only in 2009, and they were based on images from the Messenger and Mariner 10 spacecraft. The radius of this small planet is 2439.7 ± 1.0 km.Venus is almost the same as the Earth in both size and mass. Of the earth's mass, its mass is 0.815. It is known that it completes a revolution around the Sun in almost two hundred and twenty-five Earth days. There is water there, but it is much less than on Earth. After the Moon and the Sun in the sky of our planet, Venus is the third brightest luminary. The following is known about it: the surface temperature is more than four hundred degrees, the extremely high density of the atmosphere, the absence of satellites. Despite all the apparent similarities between the planet and the Earth, they have too many important differences. The surface of Venus is not visible due to the fact that it is covered with dense clouds consisting of sulfuric acid. These clouds are highly reflective. The relief was explored only thanks to radio waves.

Planetology as a science suggests that most likely at one time the planet had oceans similar to those that now exist on Earth. This planet has been little studied, despite the fact that its surface has been explored by more than one spacecraft. It should be noted that none of them worked for more than two hours due to difficult conditions. It was thanks to these spacecraft that the photographs they took of the surface of this planet first appeared on Earth. This happened in 1975.
Another planet that is much smaller when compared to Earth is Mars. It received its second name “red planet” due to the presence of iron oxide on the surface. She was named after the ancient Roman god of war. It has two natural satellites named Deimos and Phobos. Scientists from many countries are studying the “red planet”. According to them, there may be water on it, but it is not in a liquid state, which is due to the pressure on the surface being too low. This conclusion indicates that primitive life may well exist on the planet.
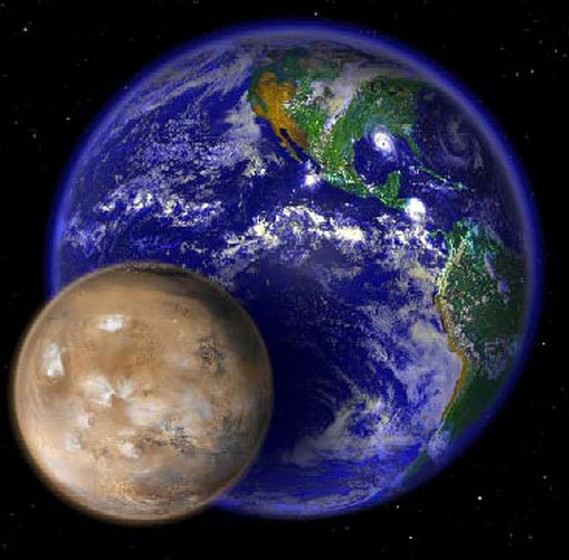

Thanks to research and the work of Mars rovers, scientists have discovered that the surface was once covered with water. The climate on the planet is seasonal, with an average temperature of minus fifty degrees. A person can easily see Mars even with the naked eye. It is known that its mass is less than eleven percent of the earth's mass.
The smallest planets in the solar system
For a long time, Pluto was considered the record-breaking planet in the solar system. However, it was no longer called a planet in 2006, in other words, it lost its status as a planet. This is due to the fact that by this time many objects had been discovered that were significantly larger than Pluto. Now, deprived of planet status, it has become one of the minor planets and is listed under number 134340 of the Central Minor Planets catalog. Time has passed, but not all scientists agreed with this; some still continue to believe that this planet should be returned to its former status. 
Officially, today the most miniature planet of ours solar system A planet called Mercury is considered. It moves much faster than other planets, most likely because of this it was given this name. After all, as you know, the god of trade Mercury was fleet-footed. Its mass is 3.3 1023 kg. Relative to the mass of the Earth, the mass of Mercury is 0.055. Considering its density, it can be argued that its depths contain a lot of metals. This small planet orbits the sun in eighty-eight Earth days.

Mercury has been studied very little, but it is known that it has no satellites. Some of its notable features include jagged, numerous slopes and impact craters.
The smallest planet in the Galaxy
Some twenty to thirty years ago, only our Solar System in the Galaxy was known with certainty. Scientists could only make assumptions about the fact that somewhere outside our system there is an almost infinite number of planetary systems of other stars. The beauty of big and small planetsWe can only be content with what is already known for sure about our solar system, namely, that the smallest planet until 2006 was Pluto, and now Mercury has taken its place.
Meanwhile, the largest planet is in the constellation Hercules.
What is it called: Mercury |
Area: 74797000 km 2
Equatorial circumference: 15,329.1 km The most nearby planet
to the Sun, since 2006 it has also received the title of the smallest planet in the solar system. This was due to the fact that Pluto was excluded from the category of full-fledged planets and was classified as a dwarf planet. The diameter of Mercury is only 4,900 km,
for comparison, for the Earth this figure is 12,742 km. And if we compare the volumes of the planets, then Mercury is only 0.05 the size of the Earth.
Research
Astronomers began observing this planet a very long time ago. The first written mentions date back to the 14th century. BC. in the document "Mul apin", compiled by Assyrian astronomers.
In 1631, scientists first observed the planet through a telescope and saw the passage of Mercury across the solar disk. At the end of the 20th century, Mercury was explored by the Mariner 10 satellite, which for the first time transmitted images of its surface. In 2008 – 2011, he examined the planet spaceship
“Messenger”, with the help of which scientists obtained images of almost the entire surface of the smallest planet, and conducted a series of geomagnetic and geological studies.
Appearance of the planet Mercury The surface of Mercury is brownish-gray in color. In terms of relief, it is very reminiscent of the Moon, since the entire outer layer is simply strewn with many craters from collisions with cosmic bodies. Scientists explain this mass destruction planets by what she has there is practically no atmosphere
, which could protect against meteorites and comets.
In addition, the planet has very long mountain ranges in the form of sharp ledges and rocks, giant surface “folds”.
The smallest planet in our solar system is Mercury
A study of the planet's surface confirmed that during the formation of the planet, many volcanoes were active across the entire surface. Evidence of such phenomena is best preserved at the north pole, since it was least exposed to attacks from cosmic bodies.
Based on the data obtained, scientists claim that the lava layer at the North Pole reaches 2 km. Lava flowed from volcanic holes formed due to damage to the outer shell. The largest lava tunnel discovered by satellite is 25 km. According to calculations, a volume of lava that could cover 200 km 2 should have flowed through such a hole.
Atmosphere
Scientists for a long time were convinced that the atmosphere on Mercury was completely absent. But during the research of Mariner 10, it was found that there are still gases on the surface of the planet, although in very small quantities.
The atmosphere of Mercury is more correctly called the exosphere. It consists of oxygen (O2), hydrogen (H2), sodium (Na), potassium (K) and helium (He). Due to weak gravity, gases do not linger at the surface of the planet and fly into outer space. According to scientists, helium and hydrogen are formed on Mercury, and other elements enter the exosphere due to solar winds.
Magnetic storms
Instead of atmospheric storms, magnetic storms often rage on Mercury. Although the planet’s magnetic field is very weak (only 1% of the power compared to Earth’s), strong magnetic tornadoes occasionally arise from interaction with solar wind particles.
Temperature
Due to the lack of a full atmosphere, the planet has the largest temperature range in the Solar System. The maximum figure is about +427°С, and the minimum is close to – 173°С.
Despite its close location to the Sun and a record high of +427°C, Venus is considered the hottest planet, since its average temperature is much higher.
Ice
Even Mercury has ice. Scientists made such assumptions back in 1991, and thanks to data from Messenger radars, they were confirmed. The ice is found in deep craters at the north and south poles in a permanent shadow zone.
North Pole of Mercury. The large Prokofiev crater is visible. There is ice in the craters. The top of the ice is covered with some organic dark substance. photo:NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington
Mercury time
One day on Mercury lasts about 176 Earth days, and a year is 88 days. Such unusual data have logical explanation. It’s just that the speed of the planet’s movement in orbit is several times higher than the speed of rotation around its own axis. And it turns out that it circles around the Sun faster than around itself.
There are versions that earlier the speed of rotation around its axis was much higher, but over time it decreases under the influence of the Sun.
Density and gravity
Although Mercury is very small, it has a high density, as it is composed of stones and iron. In the Solar System it has the second highest density level - 5.43 g/cm3. The Earth comes in first place due to its large size and centrifugal force.
The gravity on the planet is 38% of that on Earth, so if you weigh 100 kg on Earth, then on Mercury the scales will show 38 kg.
Core
Analyzing data from Messenger, researchers found that the iron core of Mercury is in a liquid state and has a radius of about 2 thousand kilometers. Which is 80% of the total radius of the planet. Such proportions between the core and other layers are not observed in any known planet.
How is the phenomenon of a large nucleus explained?
There are 2 working versions:
- Mercury was originally 2.25 times its current size. After a collision with a large cosmic body, it lost most of its outer layers and took on its current appearance.
- At the time of the formation of the planet, the Sun carried light elements into distant areas interplanetary space, which is why its structure is saturated with such dense substances.
Mercury decreases
According to astronomers, Mercury's core is gradually cooling and shrinking in size. This is the cause of massive earthquakes and a decrease in the size of the planet. Proof of this are the long steep ledges on its surface.
Unique orbital motion
Mercury is also distinguished by the nature of its orbital movement - it has a variable speed of movement. At a distance from the Sun it moves slowly, but in the area next to it it speeds up significantly. This feature of Mercury led to the fact that the Sun stops for a while and begins to move in the opposite direction.
To be fair, it is worth noting that its rotation around its axis is constant.
Walking across the solar disk
Since Mercury is closest to the Sun, it is extremely difficult to see from Earth. Except at dawn or dusk. But 13 times per century the small planet passes across the solar disk. In the 21st century, he did this twice already – on 05/07/2013 and 11/08/2006. The next similar event will take place on 05/09/2016 and 11/11/2019.
Mercury is the smallest planet in our solar system. NASA's clearest image of Mercury was taken during the Messenger mission. The colors are intentionally more saturated.
- From Mercury to the Sun there are about 58 million km.
- To reach Mercury's orbit, Messenger traveled 79 million km and was forced to circle the Sun 15 times to synchronize with the planet.
- When Mercury is at its closest to the Sun, it is 3 times larger than what we see from Earth.
- Thanks to lower gravity, a person on Mercury would be able to jump 2.6 times higher than on our planet.
- A spaceship flies from Earth to Mercury in 6 years.
- Mercury's radio signal to Earth and back will return in 5 minutes.
- In terms of size, the small planet is inferior even to some of the satellites of the giant planets, for example, Titan and Ganymede.
- Mercury's core is comparable to the size of the Moon.
- Near the two poles of the planet there are areas that are never hit by the sun's rays.
- It is estimated that the ice layer on Mercury reaches 2 m.
- Only on Mercury can you observe how the Sun rises (or sets) twice in one day.
- The largest Mercury crater has a diameter of 716 km; researchers named it Rembrandt.
- The largest ledge, called Discovery, is 350 km long and 3 km high.
- At a level of 1 m under the outer shell of Mercury there are no temperature fluctuations. Here it is constantly at +75°C.
- The planet has a comet-like tail, the length of which exceeds 2.5 million km.
- If the Earth were empty inside, it would fit 20 Mercurys
Jupiter and Earth in comparison
- Equatorial circumference: 15,329.1 km big planet Solar System - Jupiter. It is the fifth planet from the Sun and is more than 2.5 times heavier than all the other planets combined! Jupiter's equator is approximately 11 times the diameter of the Earth, its length is 143,884 km!
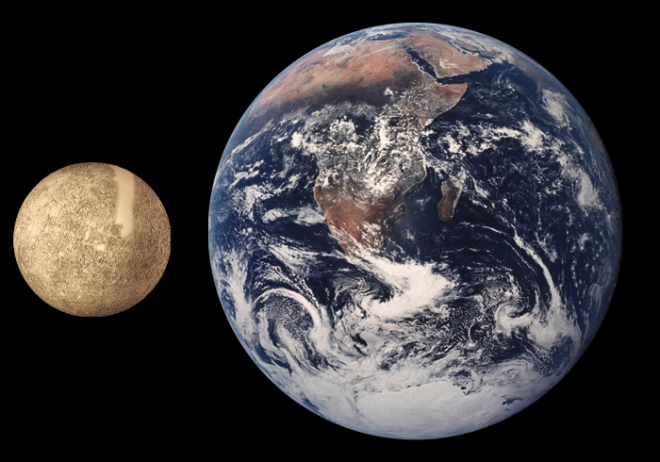

Mercury and Earth in comparison
- The smallest planet in the solar system is Mercury. Its diameter is only 4789 km. It is even smaller in size than some of its satellites, such as Jupiter's Ganymede and Saturn's Titan.
- It is paradoxical that big planet- Jupiter, the smallest satellite of all known. It is called Leda and has a diameter of 10 km.
- Pallas is the largest asteroid. Diameter – 490 km. Until 2006, Ceres was considered the largest asteroid, until it was given the status of a dwarf planet.

- One of the most interesting riddles of the sun- This is the solar corona (the outer part of the atmosphere), the temperature of which is higher than that of the star itself.
- Jupiter breaks all records in the solar system. He has the most a large number of satellites - 63! Its closest competitor is Saturn with 60 satellites.
- The brightest planet in the solar system is Venus. More precisely, this is a planet that reflects greatest number sunlight– 76%. This property is due to special clouds in the atmosphere of Venus. This is the third brightest object in the Earth's sky, second only to Venus to the Sun and Moon.

- Brightest comet with the prosaic name C/1910 A1, it surpasses even Venus in brightness. It is also known as the Great January Comet, as it was discovered in January 1910.
- The brightest asteroid- Vesta. It is the only asteroid that can be seen with the naked eye in the night sky.
- The coldest place Solar system - Neptune's satellite, Triton. There it is 38 degrees warmer than absolute zero, that is -235.
- Neptune – windiest planet. Large atmospheric formations on Neptune's equator move at a speed of 320 m/s, and smaller ones move 2 times faster.

Pluto is no longer the last planet in the solar system
- Until August 24, 2006, it was believed that there were 9 planets in the Solar System. But now there are 8 of them because the International Astronomical Union excluded dwarf Pluto from the list. But now there's been a new study that suggests Pluto may need a reclassification again. So in the near future there may be 9 planets again!
The largest planet in the solar system
Jupiter. Its equatorial diameter is 143884 km, which is 11.209 times the diameter of the Earth and is 0.103 times the diameter of the Sun. Jupiter's shape is not entirely spherical because the planet is made of gas and liquid and rotates rapidly. The polar diameter of Jupiter is 133,708 km. The mass of Jupiter is 318 times the mass of the Earth and 2.5 times the mass of all other planets combined. Jupiter is only 1047 times less massive than the Sun.
The smallest planet in the solar system
Pluto. Its diameter is only 2400 km. The rotation period is 6.39 days. The mass is 500 times less than the earth's.
Has a satellite, Charon, discovered by J. Christie and R. Harrington in 1978.
Venus. Its maximum magnitude is -4.4.
Venus comes closest to Earth and, in addition, reflects sunlight most effectively, since the planet's surface is covered with clouds. The top layers of the clouds of Venus reflect 76% of the sunlight falling on them.
When Venus appears brightest, it is in its crescent phase. Venus's orbit lies closer to the Sun than the Earth's, so Venus's disk is only fully illuminated when it is on the opposite side of the Sun. At this time, the distance to Venus is greatest, and its apparent diameter is smallest.
The largest satellite in the solar system
Ganymede is a satellite of Jupiter with a diameter of 5262 km. Saturn's largest moon, Titan, is the second largest (its diameter is 5,150 km), and at one time it was even thought that Titan was larger than Ganymede. In third place is Jupiter's satellite, Callisto, adjacent to Ganymede. Both Ganymede and Callisto are larger than the planet Mercury (which has a diameter of 4878 km).
Ganymede owes its status as the "largest moon" to the thick mantle of ice that covers its rocky interior. The solid cores of Ganymede and Callisto are likely similar in size to Jupiter's two small inner Galilean moons, Io (3,630 km) and Europa (3,138 km).
The smallest satellite in the solar system Deimos is a satellite of Mars. The smallest satellite, the dimensions of which are precisely known, Deimos, roughly speaking, has the shape of an ellipsoid with dimensions of 15x12x11 km. Its possible rival is Jupiter's moon Leda, which is estimated to be about 10 km in diameter. The largest asteroid in the solar system
Ceres. Its dimensions are 970x930 km. In addition, this asteroid was the very first to be discovered. It was discovered by Italian astronomer Giuseppe Piazzi on January 1, 1801. The asteroid got its name because Ceres, a Roman goddess, was associated with Sicily, where Piazzi was born. The next largest asteroid after Ceres is Pallas, discovered in 1802. Its diameter is 523 km.
Vesta. Its brightness reaches magnitude 5.5.
In very dark skies, Vesta can even be seen with the naked eye (it is the only asteroid that can be seen with the naked eye at all). The next brightest asteroid is Ceres, but its brightness never exceeds magnitude 7.3. Although Vesta is more than half the size of Ceres, it is much more reflective. Vesta reflects about 25% of the sunlight falling on it, while Ceres reflects only 5%.
The largest crater on the Moon Hertzsprung. Its diameter is 591 km and it is located on back side Moons. This crater is a multi-ringed impactor. Similar impact structures on visible side
The moons were later filled with lava, which hardened into dark, hard rock. These features are now commonly referred to as maria rather than craters. However, no such volcanic eruptions occurred on the far side of the Moon.
The most famous comet
Sightings of Halley's Comet have been traced back to 239 BC. No other comet has a historical record that compares to Halley's Comet. Halley's Comet is unique: it has been observed 30 times over more than two thousand years. This is because Halley's comet is much larger and more active than other periodic comets. The comet is named for Edmund Halley, who in 1705 realized the connection between several previous appearances of the comet and predicted its return in 1758-59. In 1986, the Giotto spacecraft was able to image the nucleus of Halley's Comet from a distance of only 10 thousand kilometers. It turned out that the core is 15 km long and 8 km wide.
The brightest comets
The brightest comets of the 20th century include the so-called “Great Daylight Comet” (1910), Halley’s Comet (when it appeared in the same 1910), comets Schellerup-Maristany (1927), Bennett (1970) , Vesta (1976), Heil-Bopp (1997). The brightest comets of the 19th century are probably the "Great Comets" of 1811, 1861, and 1882. Previously, very bright comets were recorded in 1743, 1577, 1471 and 1402. The closest (and brightest) appearance of Halley's Comet was noted in 837.
Lexel. The closest distance to Earth was reached on July 1, 1770 and was 0.015 astronomical units (i.e. 2.244 million kilometers or about 3 times the diameter of the Moon's orbit). When the comet was closest, the apparent size of its coma was almost five times the diameter. full moon. The comet was discovered by Charles Messier on June 14, 1770, but received its name from Anders Johann (Andrei Ivanovich) Leksel, who determined the orbit of the comet and published the results of his calculations in 1772 and 1779. He found that in 1767 the comet came close to Jupiter and, under its gravitational influence, moved into an orbit that passed close to the Earth.
Longest total solar eclipse
Theoretically, the total phase of an eclipse can take up the entire duration of totality. solar eclipse- 7 minutes 31 seconds. In practice, however, such long eclipses have not been recorded. The longest total eclipse
in the recent past there was an eclipse on June 20, 1955. It was observed from the Philippine Islands, and the total phase lasted 7 minutes 8 seconds. The longest future eclipse will take place on July 5, 2168, when the total phase will last 7 minutes 28 seconds.
Nearest star
Equatorial circumference: 15,329.1 km Proxima Centauri. It is located 4.25 light years from the Sun. It is believed that, together with the double star Alpha Centauri A and B, it is part of a free triple system. The double star Alpha Centauri is a little further away from us, at a distance of 4.4 light years.
The Sun lies in one of the spiral arms of the Galaxy (the Orion Arm), at a distance of about 28,000 light years from its center. At the location of the Sun, the stars are usually several light years apart from each other. bright Star Sirius. Its magnitude is -1.44. Sirius got its name from Ancient Greece to which he belongs.
At just 8.7 light-years away, Sirius is one of the closest stars to the Sun.
The next brightest star after Sirius is Canopus in the constellation Carina, which has a magnitude of -0.72. In fact, Sirius is a system of two stars revolving around each other. Almost all of the light comes to us from the main star, which is called Sirius A and is a white normal star about 2.3 times more massive than the Sun. The fainter companion, Sirius B, discovered by visual observation in 1862, is a white dwarf. The light from Sirius B is only one ten-thousandth of the light from Sirius A. The Sirius binary system completes one revolution every 50 years.
The most powerful star in terms of radiation
Star in a Pistol. In 1997, astronomers working with the Hubble Space Telescope discovered this star.
They named it the "Star in a Pistol" after the shape of the nebula surrounding it. Although the radiation from this star is 10 million times more powerful than that of the Sun, it is not visible to the naked eye because it is located near the center of the Milky Way at a distance of 25,000 light years from Earth and is hidden by large clouds of dust.
Before the discovery of the Pistol Star, the most serious contender was Eta Carinae, which was 4 million times more luminous than the Sun.
Biggest star
A star from the constellation Lupus observed in 1006 AD. Based on many surviving observational records, it can be established that the apparent magnitude of the supernova was about -10, which is comparable to the Moon. The position of this supernova was identified by a known supernova remnant (number PKS 1459-41), which emits radio waves and X-rays and is observed in the optical range as faint filaments. The distance to the supernova is estimated at 3260 light years. At their maximum brightness, all supernovae reach approximately the same absolute magnitude, but their apparent brightness depends on both the distance and the amount of dust in the path of the light beam. The next brightest (after the supernova of 1006) is the explosion of 1054, which created the Crab Nebula in Taurus. This supernova reached an apparent magnitude of -5.
Largest known globular cluster
Omega Centauri. It contains millions of stars, concentrated in a volume with a diameter of about 620 light years. The shape of the cluster is not entirely spherical: it looks slightly flattened. In addition, Omega Centauri is also the brightest globular cluster in the sky with a total magnitude of 3.6. It is 16,500 light years away from us.
The name of the cluster has the same form as the names of individual stars usually have. It was assigned to the cluster in ancient times, when it was impossible to recognize the true nature of the object when observing with the naked eye. Omega Centauri is one of the oldest clusters.
Nearest galaxy
The dwarf galaxy in the constellation Sagittarius is the closest galaxy to the Milky Way Galaxy. This small galaxy is so close that the Milky Way seems to be swallowing it up. The galaxy lies 80,000 light-years from the Sun and 52,000 light-years from the center of the Milky Way. The next closest galaxy to us is the Large Magellanic Cloud, located 170 thousand light years away.
The most distant object that can be seen with the naked eye is the Andromeda Galaxy (M31). It lies about 2 million light-years away and is about the brightness of a 4th magnitude star. It is a very large spiral galaxy, the largest member of the Local Group, to which our own Galaxy belongs. Besides it, only two other galaxies can be observed with the naked eye - the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds. They are brighter than the Andromeda Nebula, but much smaller and less distant (at 170,000 and 210,000 light years, respectively). However, it should be noted that sharp-sighted people in dark night
can see the M31 galaxy in the constellation Ursa Major, the distance to which is 1.6 Megaparsecs.
Largest constellation
Hydra. The area of the sky included in the constellation Hydra is 1302.84 square degrees, which is 3.16% of the entire sky. The next largest constellation is Virgo, occupying 1294.43 square degrees. Most of the Hydra constellation lies south of the celestial equator, and its total length is more than 100°. Despite its size, Hydra does not stand out particularly in the sky. It mainly consists of fairly faint stars and is not easy to find. The brightest star is Alphard, a second-magnitude orange giant located 130 light-years away.
Smallest constellation
South Cross. This constellation occupies an area of the sky of only 68.45 square degrees, which is equivalent to 0.166% of the entire sky area. Despite its small size, the Southern Cross is a very prominent constellation that has become a symbol of the southern hemisphere. It contains twenty stars brighter than magnitude 5.5. Three of the four stars that form his cross are 1st magnitude stars. The Southern Cross constellation contains an open star cluster (Kappa Crucis, or "Jewel Box" cluster), considered by many observers to be one of the most beautiful in the sky. The next smallest constellation (more precisely, occupying 87th place among all constellations) is the Lesser Horse. It covers 71.64 square degrees, i.e. 0.174% of the sky area.
The largest optical telescopes Two Keck Telescopes located side by side on the summit of Mauna Kea, Hawaii. Each of them has a reflector with a diameter of 10 meters, made up of 36 hexagonal elements. From the very beginning they were intended for. Since 1976, the largest optical telescope with a solid mirror has been the Russian Large Azimuth Telescope. Its mirror has a diameter of 6.0 m. For 28 years (1948 - 1976), the largest optical telescope in the world was the Hale Telescope on Mount Palomar in California. Its mirror has a diameter of 5 m. Very Large Telescope, located in Cerro Paranal in Chile, is a structure of four mirrors with a diameter of 8.2 m, which are connected together to form a single telescope with a 16.4-meter reflector.
The world's largest radio telescope
Arecibo Observatory radio telescope in Puerto Rico.
It is built into a natural depression on the earth's surface and has a diameter of 305 m. The world's largest fully controlled radio antenna is the Green Bank Telescope in West Virginia in the USA. Its antenna diameter is 100 m. The largest radio telescope array located in one place is the Very Large Array (VLA), which consists of 27 antennas and is located near Socorro in New Mexico, USA. In Russia, the largest radio telescope is "RATAN-600" with a diameter of 600 meters of antenna-mirrors installed around the circumference.
Nearest galaxies
Astronomical object number M31, better known as the Andromeda nebula, is located closest to us than all other giant galaxies. In the Northern Hemisphere sky, this galaxy appears the brightest from Earth. The distance to it is only 670 kpc, which in our usual measurements is a little less than 2.2 million light years. The mass of this galaxy is 3 x 10 times the mass of the Sun. Despite its enormous size and mass, the Andromeda nebula is similar to the Milky Way. Both galaxies are giant spiral galaxies. The closest to us are the small satellites of our Galaxy - the Large and Small Magellanic clouds of irregular configuration. The distance to these objects is 170 thousand and 205 thousand light years, respectively, which is negligible compared to the distances used in astronomical calculations. Magellanic clouds are visible to the naked eye in the sky in the Southern Hemisphere.
Among astrophysicists who have devoted their creative work to the study of distant galaxies, H. Spinrad, an employee of the University of California at Berkeley, stands out. He is responsible for the discoveries of more than one ultra-distant galaxy. Initially, Spinrad in 1975 discovered the record-breaking galaxy in the northern direction of the Pleiades star cluster, located at a distance of 8 billion light years from us. This galaxy is listed in the star catalog as number 3G 123. It has the strongest level of radio emission, exceeding the strength of such radiation from other giant galaxies by about 6 times.
In another series of observations carried out in 1984 using the 4-meter reflector of the KittPeak National Observatory in American state Arizona, Spinrad discovered a number of radio galaxies, including the most distant ones known to science.
Optical radiation, for example, from the radio galaxy 3S 256 reaches the Solar System over a long period of 10 billion years. In addition, the distance continues to increase, as it moves away from us at a speed of 200 thousand km/s. Unlike other nearby radio galaxies with pronounced elliptical shapes, this one has an irregularly elongated configuration. A more or less clear image of another record-breaking galaxy in terms of distance was recently obtained by American astronomers K. Chambers and J. Mealy at the Leiden Observatory.
It is no coincidence that astrophysicists pay close attention to ultra-distant astronomical objects.
By processing information collected over more than one billion light years, it is possible to form a generalized idea of the distant past of star formations, especially at the initial stages of their formation and origin, during the period corresponding to the beginning of the process of expansion of the Universe.
A group of astronomers from the University of Washington has discovered the most distant star in our Galaxy - an 18-magnitude red giant. This star is located in the direction of the constellation Libra and is distant from the Earth at a distance that light can travel in 400 thousand years. It is clear that this star is located at the boundary line, in the so-called galactic halo zone. After all, the distance to this star is approximately 4 times the diameter of the imaginary expanses of our Galaxy. (The diameter of the Milky Way is estimated at about 100 thousand light years.) It is surprising that the most distant, fairly bright star was discovered only in our time, although it had been observed before. For unknown reasons, astronomers did not pay much attention to the faintly luminous spot on the starry sky and visible on the photographic plate. What happens? People see the star for a quarter of a century and... do not notice it. More recently, American astronomers from the Lowell Observatory discovered another of the most distant stars in the peripheral reaches of our Galaxy. This star, already dimmed from “old age,” can be searched in the sky in the location of the constellation Virgo, at a distance of approximately 160 thousand light years.
Such discoveries in the dark (literally and figuratively) areas of the Milky Way allow us to make important adjustments in determining the true values of the mass and size of our star system in the direction of their significant increase. And this can seriously affect the cosmological picture of the universe accepted in the scientific community.
Most open star cluster
Of all the star clusters, the most scattered throughout outer space is a collection of stars called the Coma of Berenices. The stars here are scattered at such vast distances from each other that they look like cranes flying in a chain. Therefore, the constellation, which is a decoration of the starry sky, is also called the “Wedge of Flying Cranes.”
Superdense galaxy clusters It is known that the Milky Way galaxy, together with the Solar system, is located in a spiral galaxy, which in turn is part of a system formed by a cluster of galaxies. There are many such clusters in the Universe. I wonder which galaxy cluster is the densest and largest? According to scientific publications, scientists have long suspected the existence of giant supersystems of galaxies. IN The problem of superclusters of galaxies in a limited space of the Universe is attracting increasing attention of researchers. And primarily because studying this issue can provide additional important information about the birth and nature of galaxies and radically change existing ideas about the origins of the Universe.
Over the past few years, giant star clusters have been discovered in the sky. The densest cluster of galaxies in a relatively small area of world space was recorded by American astronomer L. Cowie from the University of Hawaii. This supercluster of galaxies is located at a distance of 5 billion light years from us. It emits as much energy as several trillion celestial bodies like the Sun combined could produce.
At the beginning of 1990, American astronomers M. Keller and J. Haykr identified a super-dense cluster of galaxies, which was given the name “Great Wall”, by analogy with the Great Wall of China. The length of this stellar wall is approximately 500 million light years, and its width and thickness are 200 and 50 million light years, respectively.
The formation of such a star cluster does not fit into the generally accepted big bang theory of the origin of the Universe, from which the relative uniformity of the distribution of matter in space follows. This discovery posed a rather difficult task for scientists. It should be noted that the closest galaxy clusters to us are located in the constellations Pegasus and Pisces at a distance of only 212 million light years. But why are galaxies located at a greater distance from us in denser layers relative to each other than in the parts of the Universe closest to us, as expected? Above this difficult question
Astrophysicists are still scratching their heads.
Nearest star cluster
The closest open star cluster to the Solar System is the famous Hyades in the constellation Taurus. It looks good against the background of the winter starry sky and is recognized as one of the most wonderful creations of nature.
Black holes often involve nearby cosmic bodies in rotational motion around them. The unusually rapid rotation of astronomical objects around the center of the Galaxy, which is 300 million light-years away from us, was discovered quite recently. By according to experts, such an ultra-high speed of rotation of bodies is due to the presence in this part of the world space of a supermassive black hole, the mass of which is equal to the mass of all the bodies of the Galaxy taken together (approximately 1.4x1011 solar masses). But the fact is that such mass is concentrated in a part of space 10 thousand times smaller than our Milky Way star system. This astronomical discovery so amazed American astrophysicists that it was decided to immediately begin a comprehensive study of the supermassive black hole, the radiation of which is closed in on itself by powerful gravity. For this purpose, it is planned to use the capabilities of an automatic gamma observatory launched into low-Earth orbit. Perhaps such determination of scientists in studying the mysteries of astronomical science will finally make it possible to clarify the nature of mysterious black holes.
Largest astronomical object
The largest astronomical object in the Universe is noted in star catalogs under the number ZS 345, registered in the early 80s. This quasar is located 5 billion light years from Earth.
German astronomers, using a 100-meter radio telescope and a fundamentally new type of radio frequency receiver, measured such a distant object in the Universe.
The results were so unexpected that scientists did not believe them at first. It's no joke, the quasar was 78 million light years across. Despite such a great distance from us, when observed, the object appears twice as large as the lunar disk.
Largest galaxy
However, as the subsequent development of astronomy showed, even larger galaxies were listed in star catalogs. From a large class of weakly luminous formations in the Metagalaxy, called Markarian galaxies, galaxy number 348, discovered a quarter of a century ago, was isolated. But then the size of the galaxy was clearly underestimated. Later observations by American astronomers using a radio telescope located in Socorro, New Mexico, made it possible to establish its true size. The record holder has a diameter of 1.3 million light years, which is already 13 times the diameter of the Milky Way. It is 300 million light years away from us.
The most powerful star in terms of radiation
At one time, Abell compiled a Catalog of Galactic Clusters, consisting of 2712 units. According to it, in galaxy cluster number 2029, the largest galaxy in the Universe was discovered right in the center. Its diameter is 60 times larger than the Milky Way and is about 6 million light years, and its radiation is more than a quarter of the total radiation of the galaxy cluster. Astronomers from the United States recently discovered a very large star. Research is still ongoing, but it is already known that a new record holder has appeared in the Universe. According to preliminary results, the size of this star is 3500 times greater than the size of our star. And it emits 40 times more energy than the hottest stars in the Universe.
The brightest astronomical object
In 1984, the German astronomer G. Kuhr and his colleagues discovered such a dazzling quasar (quasi-stellar source of radio emission) in the starry sky that even at a great distance from our planet, estimated at many hundreds of light years, it would not be inferior to the Sun in terms of the intensity of light emission sent to the Earth, although it is distant from us in outer space, which light can travel in 10 billion years. In its brightness, this quasar is not inferior to the brightness of ordinary 10 thousand galaxies combined. In the star catalogue, it received the number S 50014+81 and is considered the brightest astronomical object in the boundless expanses of the Universe. Despite its relatively small size, reaching a diameter of several light years, a quasar emits much more energy than an entire giant galaxy. If the radio emission of an ordinary galaxy is 10 J/s, and the optical emission is 10, then for a quasar these values are 10 and 10 J/s, respectively. Note that the nature of the quasar has not yet been clarified, although there are different hypotheses: quasars are either the remnants of dead galaxies, or, on the contrary, objects initial stage evolution of galaxies, or something else completely new.
The brightest stars
According to information that has reached us, the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus first began to distinguish stars by their brightness back in the 2nd century BC. e. To assess the luminosity of different stars, he divided them into 6 degrees, introducing the concept of stellar magnitude into use. In the very early XVII century, the German astronomer I. Bayer proposed to designate the degree of brightness of stars in different constellations with letters of the Greek alphabet. The brightest stars are called “alpha” of such and such a constellation, the next brightest stars are called “beta”, etc.
The brightest stars in our visible sky are Deneb from the constellation Cygnus and Rigel from the constellation Orion.
The luminosity of each of them exceeds the luminosity of the Sun by 72.5 thousand and 55 thousand times, respectively, and the distance from us is 1600 and 820 light years.
The star Sirius from the constellation Canis Major, which is considered the brightest among the stars closest to us, is only 23.5 times brighter than our star; the distance to it is 8.6 light years. There are even brighter stars in the same constellation. Thus, the star of Adara shines as bright as 8,700 suns combined at a distance of 650 light years. And the North Star, which for some reason was incorrectly considered the brightest visible star and which is located at the tip of Ursa Minor at a distance of 780 light years from us, shines only 6000 times brighter than the sun.
The zodiacal constellation Taurus is notable for the fact that it contains an unusual star, characterized by its supergiant density and relatively small spherical size. As astrophysicists have found out, it mainly consists of fast neutrons scattering into different sides. This star was for some time considered the brightest in the Universe.
In general, blue stars have the greatest luminosity.
The brightest star known is UW SMa, which shines 860 thousand times brighter than the Sun. Over time, the brightness of stars can change. Therefore, the star that holds the record for brightness may also change. For example, reading an ancient chronicle dated July 4, 1054, you can find out that the brightest star shone in the constellation Taurus, which was visible to the naked eye even during the day. But over time, it began to fade and within a year it disappeared altogether. Soon, in the place where the star shone brightly, a nebula very similar to a crab began to be discerned. Hence the name - the Crab Nebula, which was born as a result of a supernova explosion.
Modern astronomers have discovered a powerful source of radio emission, the so-called pulsar, in the center of this nebula. It is the remnant of that bright supernova described in the ancient chronicle.
the brightest star in the Universe is the blue star UW SMa;
the brightest star in the visible sky is Deneb;
the brightest nearby star is Sirius;
the brightest star in the Northern Hemisphere is Arcturus;
the brightest star in our northern sky is Vega;
the brightest planet in the solar system is Venus;
The brightest minor planet is Vesta.
The dimmest star
Astronomers call supernovae stellar objects that suddenly burst into flames and reach their maximum luminosity in a relatively short period of time. It has been established that the oldest evidence of a supernova explosion from all surviving astronomical observations dates back to XIV century BC e. Then ancient Chinese thinkers registered the birth of a supernova and indicated its location and time of outbreak on the shell of a large turtle. For modern researchers It was possible to determine from the armored manuscript the place in the Universe where a powerful source of gamma radiation is currently located. There is hope that such ancient evidence will help to fully understand the problems associated with supernovae and trace the evolutionary path of special stars in the Universe. Such evidence plays important role V
modern interpretation
the nature of the birth and death of stars. Shortest-lived star The discovery of a new type of X-ray star in the area of the Southern Cross and Centaurus constellations in the 70s by a group of Australian astronomers led by K. McCarren caused a lot of noise. The fact is that scientists witnessed the birth and death star, whose life expectancy was unprecedented
a short time
- about 2 years. This has never happened before in the entire history of astronomy. The suddenly flared star lost its shine in a time that was negligibly short for stellar processes. The most ancient stars Astrophysicists from the Netherlands have developed a new, more advanced method for determining the age of the oldest stars in our Galaxy. It turns out that after the so-called
big bang
According to scientists from the UK, Germany and the USA, conducting joint research, the youngest stars are located in the nebula NGC 1333. This nebula is located at a distance of 1100 light years from us. It has attracted increased attention from astrophysicists since 1983 as the most convenient object of observation, the study of which will reveal the mechanism of star birth.
Quite reliable data received from the IRAS infrared satellite confirmed astronomers' guesses about the ongoing violent processes characteristic of the early stages of star formation. At least 7 of the brightest star births were recorded somewhat south of this nebula. Among them, the youngest was identified, called “IRAS-4”. His age turned out to be quite “infantile”: only a few thousand years. It will take many more hundreds of thousands of years for the star to reach the stage of its maturation, when the conditions for raging nuclear chain reactions will be created in its core.
The smallest star
In 1986, through the efforts of mainly American astronomers from the KittPeak Observatory, a previously unknown star was discovered in our Galaxy, designated LHS 2924, whose mass is 20 times less than that of the Sun, and whose luminosity is six orders of magnitude less. This star turned out to be the smallest in our Galaxy.
Its light emission occurs as a result of the resulting thermonuclear reaction of converting hydrogen into helium.
The fastest star
In nature, pulsars, pulsating sources of radio emission, rotate the fastest. The speed of their rotation is so enormous that the light they emit is focused into a thin conical beam, which an earthly observer can register at regular intervals. The progress of atomic clocks can be verified with the greatest accuracy using pulsar radio emissions. The fastest astronomical object was discovered by a group of American astronomers at the end of 1982 using the large radio telescope at Arecibo on the island of Puerto Rico. This is a super-fast-rotating pulsar with the assigned designation PSR 1937+215, located in the constellation Vulpecula at a distance of 16 thousand light years. In general, pulsars have been known to mankind for only a quarter of a century. They were first discovered in 1967 by a group of English astronomers led by Nobel laureate E. Hewish as sources of pulsating with high precision electromagnetic radiation . The nature of pulsars is not fully understood, but many experts believe that they are neutron stars rapidly rotating around their own axis, exciting strong magnetic fields. But the newly discovered record-breaking pulsar rotates at a frequency of 642 rps. The previous record belonged to a pulsar from the center of the Crab Nebula, which produces strictly periodic pulses of radio emission with a period of 0.033 rps. While other pulsars usually emit waves in the radio range from meter to centimeter, this pulsar also emits in the X-ray and gamma-ray ranges.
Until recently, it was believed that the limiting speed of propagation of any physical interactions was the speed of light. According to experts, there should not be a speed of movement higher than 299,792,458 m/s, with which light propagates in a vacuum. This follows from Einstein's theory of relativity. True, recently many prestigious scientific centers have increasingly begun to declare the existence of superluminal movements in global space. For the first time, superluminal data were obtained by American astrophysicists R. Walker and J. M. Benson in 1987. While observing the radio source ZS 120, located at a considerable distance from the galactic core, these researchers recorded the speed of movement of individual elements of the radio structure exceeding the speed of light. A thorough analysis of the combined radio map of the ZS 120 source gave a linear velocity value of 3.7 ± 1.2 times the speed of light. Scientists have not yet operated with large values of movement speeds.
The strongest gravitational lens in the Universe
The phenomenon of a gravitational lens was predicted by Einstein. It creates the illusion of a double image of an astronomical object of radiation through a powerful gravitational field located in the path of the source, bending the rays of light. For the first time, Einstein's hypothesis received real confirmation in 1979. Since then, a dozen gravitational lenses have been discovered. The strongest of them was discovered in March 1986 by American astrophysicists from the Kittpik Observatory, led by E. Turner. When observing one quasar, distant from the Earth at a distance of 5 billion light years, its bifurcation was recorded, separated by 157 arc seconds. This is a fantastic amount. Suffice it to say that other gravitational lenses lead to a split image lasting no more than seven arc seconds. Apparently, the reason for such a colossal split in the image is a supermassive black hole, which is 1000 times heavier than our Galaxy, as a result of which a powerful gravitational field is created in this part of the space of the Universe.
The most powerful magnet in the Universe
The strongest magnetic field in the Universe is formed in the vicinity of a fifteenth-magnitude star with the astronomical designation PG 1031+234. It is a white dwarf about the same size as Earth, but located 100 light years away from the star. American astrophysicists from the University of Arizona in the mid-80s determined the magnitude of magnetic induction in this region of space and... could not believe it. The instrument readings were at the level of 70 thousand tesels, or in Gaussian units - 700 million. Such a strong magnetic field
has not yet been observed in the Universe.
Unique gas and dust clouds in space
At the end of the 70s, information appeared in the press about the discovery of a giant gas and dust cloud in interstellar space. According to scientists, the mass of this cloud is a trillion times greater than the mass of the Sun (1.9889x1030 kg). This is the largest gas and dust cloud in the Universe. And the brightest gas and dust cloud in interstellar space is the Orion Nebula.
The mass of the superhot gas cloud exceeds the mass of the Sun by 300 times, and it is located at a distance of approximately 1.5 thousand light years from us.
The largest hydrogen cloud in the Universe
An impressively large cloud of neutral hydrogen was discovered in the Universe quite by accident while solving other astronomical problems at Arecibo by American astronomers from Cornell University. The diameter of this cloud is 10 times larger than our Galaxy, and the hydrogen mass in the cloud is almost a billion times larger than the mass of our star. The cloud is located towards the constellation Leo at a distance of 65 million light years from Earth and rotates around the center of mass at a speed of 80 km/s. As scientists suggest, the birth of a new galaxy is possible from this giant hydrogen cloud. This casts doubt on the widespread big bang theory of the simultaneous birth of all galaxies after a colossal explosion in the Universe. The most abundant substance in interstellar space More than 60 molecules have been identified in the lifeless interstellar medium. chemical substances. Most of all, hydrogen is found in interstellar space. In terms of prevalence, hydrogen is far ahead of the total content of all other
chemical elements
Black holes are the densest clusters of astronomical objects. The densest clusters of cosmic objects are the so-called black holes, predicted by the theory of relativity. In outer space, the emergence of black holes occurs as a result of colossal gravitational compression of supermassive astronomical objects. The compression is so strong that the resulting gravitational field does not even let light radiation out of its zone of influence. According to astrophysicists, the cosmic density in black holes reaches 5x10 Mg/m. This is such a huge quantity that it is difficult to imagine or compare with measured quantities in nature. For comparison: the density of a neutron star and the density of an atomic nucleus is 10.4 Mg/m, and the Sun is only 1.4 Mg/m. The average density in an ordinary galaxy is 2x1 Mg/m, and in the entire Universe it is presumably 10 Mg/m.
Mercury - on this moment It is considered the smallest of all known planets in the Solar System.

It rotates around the Sun at a distance of 47 million km in a highly elongated elliptical orbit with an average speed of 48 km/s. There is relatively little information about this planet today, this is due to the fact that Mercury is located very close to the Sun, and this greatly complicates the process of its study.
Global map of Mercury compiled using the MESSENGER apparatus
Record temperature changes

This smallest planet in the solar system has the largest surface temperature differences known in this system. This is due to its close proximity to the Sun, the absence of an atmosphere and the relatively slow rotation of the planet itself. Its average daytime temperature is approximately 350 °C above zero, and its nighttime temperature is around 170 °C below zero. The minimum recorded temperature on Mercury is minus 183 °C, and the maximum, achieved in the middle of the day at “hot longitudes” when the planet is located near perihelion, is plus 427 °C. Despite these conditions, modern scientists have suggested the existence of ice on the surface of Mercury.
Small, but remote...
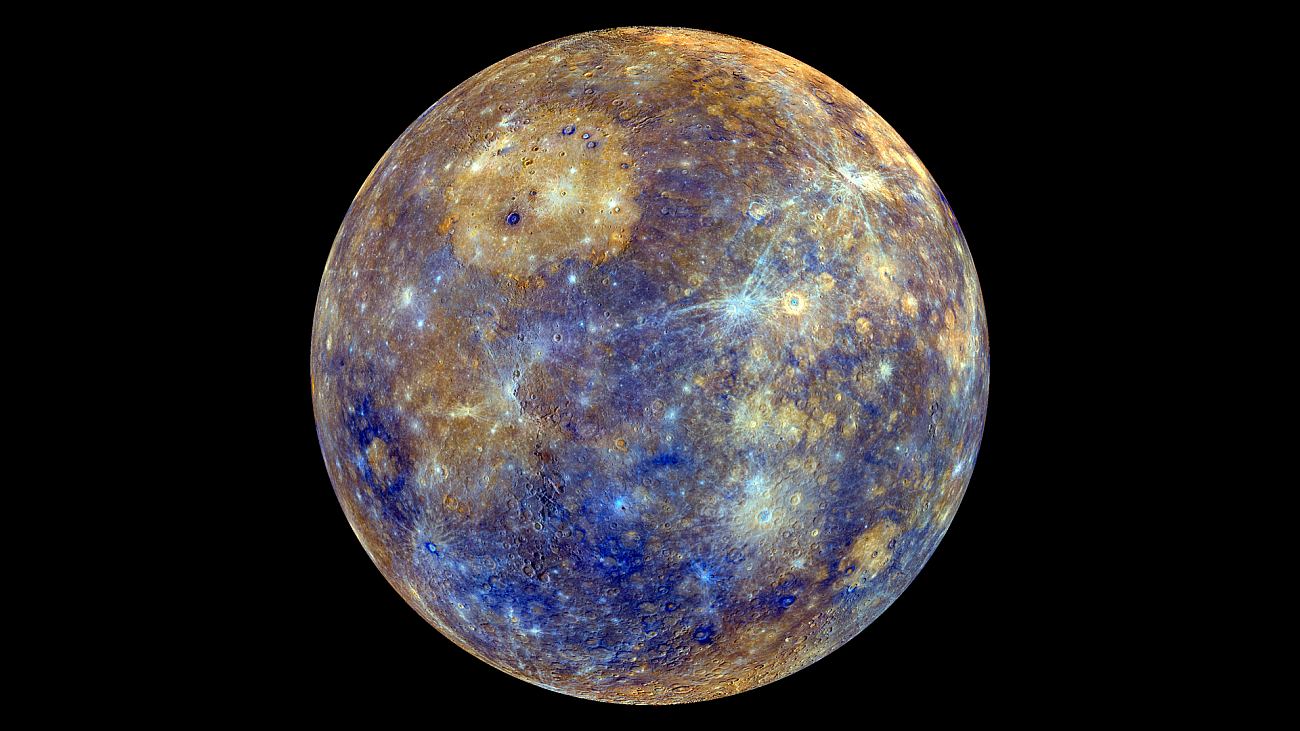
Mercury is also the smallest planet in the terrestrial group. Its circumference is only 4879.4±1.0 km, which is less than the circumference of Ganymede, a satellite of Jupiter, and Titan, a satellite of Saturn. But, despite its significantly smaller size, due to its huge core, the smallest planet still exceeds these satellites of the giant planets in its mass, which is 3.3 × 10 to the 23rd power of kg. The average density of the relatively small Mercury is slightly less than the density of the much larger Earth and is 5.43 g/cm³, thereby indicating a high content of metals in its interior.
There is no atmosphere and never has been
According to the characteristics of the surface, Mercury is practically a twin of the Moon; it is also very heavily covered with numerous craters, but at the same time its surface is absolutely homogeneous, which serves as its distinctive feature from the Moon or Mars, which have a strong difference between one hemisphere and the other. The lack of surface erosion almost completely rules out theories that Mercury ever had a significant atmosphere. According to available data, the pressure of the atmosphere of this planet is currently 5×10 to 11 times less than the pressure of the Earth’s atmosphere.
Refuting the presence of a metallic core on Mercury
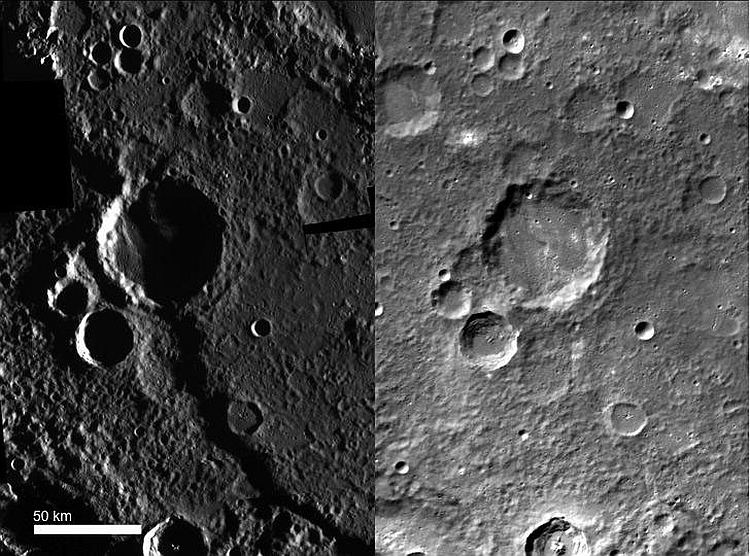

Canyon on Mercury. Lighting sometimes helps reveal amazing details
Until recently, scientists believed that Mercury consists of a metal core with a radius of approximately 1900 km, located in the depths and forming 60% of the total mass of the planet, and the surface of this core is covered by a silicate shell approximately 600 km thick. These assumptions were made due to the fact that during the research a very weak magnetic field was discovered, and it was believed that a planet of such small size could not have a liquid core.

But already in 2007, a team of leading astronomers led by Jean-Luc Margot, having analyzed the results of five years of radar observations of this space object, during which they discovered rotation variations that were too large for a planet with a solid core, refuted this theory.
Popular science film about Mercury from the European Space Agency




